Commands
PennController has three types of commands:
- Element commands: Used within a trial and called on an element
- Global commands: Used outside of a trial
- Special commands: Used within a trial, but not called on an element.
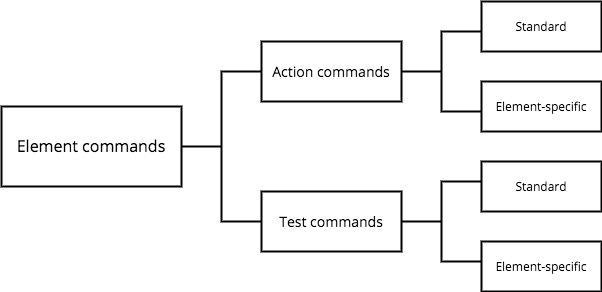
Element commands
There are two types of element commands:
- Action command: Directly manipulates an element
- Test command (PennController equivalent of a conditional statement): Runs a test on an element, and executes different code blocks depending on the success or failure of the test.
Action commands and test commands can be standard or element-specific:
- Standard: Can be called on any element without causing a runtime error.
- Element-specific: Can only be called on a specific type of element. Otherwise, causes an error.
Prefixes
Throughout this documentation, you’ll see commands with the prefix standard., like standard.print or standard.center. You’ll also see commands with the prefix X., where X is a type of element, like timer.start or button.once.
The standard. prefix indicates that the command is a standard element command, and the X. prefix indicates that the command is an element-specific command.
However, these prefixes are used only for illustrative clarity.
The standard. and X. prefixes are not part of PennControlller syntax and cannot be used inside an actual PennController script.
Action commands
Action commands do at least one of three things:
- Manipulate an element’s visual content
- Trigger an element-related event
- Control an element’s interaction with the participant
Examples of action commands:
standard.print: Prints the element to the screen (manipulates visual content). By default, the element is aligned with the left edge of the screen.@newText("text", "Hello, world!") $ .print()timer.start: Starts the Timer element (triggers an event).@newTimer("timer", 1000) $ .start()button.wait: Pauses experiment script execution until the participant clicks the Button element. (controls participant interaction).@newButton("button", "Hello, button!") @ .print() $ .wait()
In the third example, we called standard.print and button.wait on the Button element, and we crucically called standard.print before calling button.wait. Remember, PennController scripts are evaluated and executed from top to bottom.
Printing the Button element before pausing experiment script execution means that there is in fact a Button for the participant to click. If we call button.wait before calling standard.print, the experiment script execution pauses right before actually printing the Button – there would be no Button for the participant to click, and the experiment would stay paused forever.
Pay attention to the order in which you call your element commands, especially when calling a command that will pause experiment script execution!
Test commands
Test commands define conditional branching by running a test on an element:
- If the test succeeds, PennController executes the code block defined by the
successkeyword. - If the test fails, PennController executes the code block defined by the
failurekeyword.
For example, the test command button.test.clicked tests whether the Button it is called on has ever been clicked. It succeeds if, at the time of testing, the Button has been clicked at least once. It fails if the Button has never been clicked:
@newButton("big-red-button", "I'm a big red button")
@ .css({"background-color": "red", "font-size": "large"})
@ .center()
@ .print()
@,
@newButton("continue", "Click to continue")
@ .print()
@ .center()
@ .wait()
@,
@getButton("big-red-button")
$ .test.clicked()
$ .success(newText("success", "You clicked the big red button").print())
$ .failure(newText("failure", "You didn't click the big red button").print())
-
In this example, there are two Button elements, one named
"big-red-button"and one named"continue". Both Buttons are printed to the screen by thestandard.printcommand.The
"continue"Button pauses the experiment until the participant clicks on it. After the participant clicks the"continue"Button, PennController uses thegetButton()function to refer back to the"big-red-button"Button, and calls the test commandbutton.test.clickedon it. - If the participant clicked on the
"big-red-button"Button before clicking the"continue"button, the test succeeds and thesuccesscode block is executed. PennController creates a newTextelement named"sucess", and prints the string"You clicked the big red button"to the screen:@getButton("big-red-button") @ .test.clicked() $ .success(newText("success", "You clicked the button").print()) @ .failure(newText("failure", "You didn't click the button").print()) - If the participant didn’t click on the
"big-red-button"Button before clicking the"continue"button, the test fails andfailurecode block is executed. ennController creates a newTextelement named"failure", and prints the string"You didn't click the big red button"to the screen:@getButton("big-red-button") @ .test.clicked() @ .success(newText("success", "You clicked the big red button").print()) $ .failure(newText("failure", "You didn't click the big red button").print()) -
This example also introduces the standard action commands
standard.cssandstandard.center.The
standard.csscommand applies the specified CSS styles to the element. In this example it sets the"big-red-button"Button’sbackground-colorproperty tored, and itsfont-sizeproperty tox-large.The
standard.centercommand horizontally centers an element, meaning that the two Button elements are printed to the center of the screen, instead of to the default left edge.
All test commands contain the obligatory prefix test., which distinguishes them from action commands.
@// Incorrect: The test command `button.test.clicked` is not called with the `test.` prefix
%newTrial("example-trial-one",
% newButton("button", "I'm a button")
% .clicked()
%)
@
@// Correct: The test command `button.test.clicked` is called with the `test.` prefix
~newTrial("example-trial-one",
~ newButton("button", "I'm a button")
~ .test.clicked()
~)
Default commands
Every element type has a corresponding default object that can be accessed by calling defaultX, where X is an element type. For example, the default object of the Text element type is defaultText.
A default command is set by calling an element command on an element type’s default object. Once a default command has been set, it will be called on all subsequent instances of that element type within the same trial. Instances of that element type in other trials are not affected.
newTrial("trial-one",
newText("text-one")
)
newTrial("trial-two",
defaultText
.center()
,
newText("text-two")
)
newTrial("trial-three",
)
Global commands
Global commands are the commands used outside of the trial and are regarded to the whole experiment. With the help of global commands, you can initiate recorder, add a sequence and much more. Check out more under the commands tab to find the specific command you need for your experiment. If you still couldn’t find specific command, check out support tab.
Special commands
Special commands are used within a trial, but not called on an element. Currently there are four special commands: clear, end, exitFullscreen, and fullscreen.